Derivative Sign
Limit & Continuity
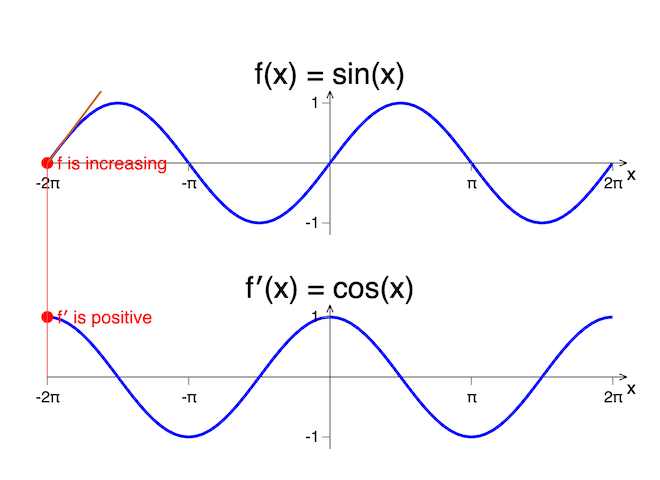
The symbol d indicates an ordinary derivative and is used for the derivative of a function of one variable, y = y(t). From the definition, if at a given point of the independent variable x the derivative is positive(negative), the function must be strictly increasing(decreasing) there. In this case, the attribute “strictly” will be omitted.
By using the mathematical language the positive(negative) sign of a derivative at a given point is sufficient (but not necessary) condition for a function to be increasing(decreasing) there.
If the derivative is zero at a given point, it means that the tangent line is parallel to the x axis and locally the function does not change. Such point is called a stationary point of the function, and is defined as a root of the derivative.