Types of Thermodynamic Systems
Thermodynamics Part 1
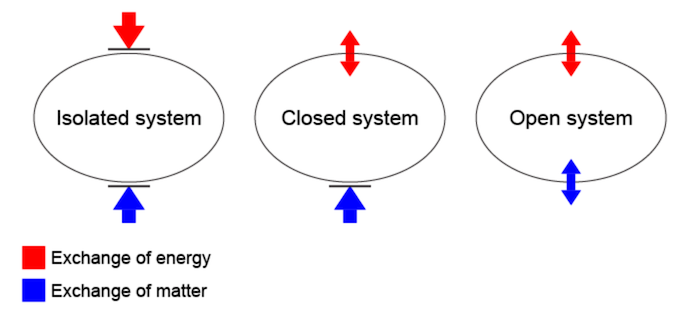
System A thermodynamic system is a specific portion of matter with a definite boundary on which our attention is focused. The system boundary may be real or imaginary, fixed or deformable. There are three types of systems: Isolated System – An isolated system cannot exchange energy and mass with its surroundings. The universe is considered an isolated system. Closed System – Across the boundary of the closed system, the transfer of energy takes place but the transfer of mass doesn’t take place. Refrigerator, compression of gas in the piston-cylinder assembly are examples of closed systems. Open System – In an open system, the mass and energy both may be transferred between the system and surroundings. A steam turbine is an example of an open system.
Entropy is the measure of the number of possible arrangements the atoms in a system can have. → Enthalpy is the measurement of energy in a thermodynamic system. Generally, thermodynamics distinguishes three classes of systems, defined in terms of what is allowed to cross their boundaries:
Thermodynamic Process A system undergoes a thermodynamic process when there is some energetic change within the system that is associated with changes in pressure, volume and internal energy. There are four types of thermodynamic processes that have their unique properties, and they are: Adiabatic Process – A process where no heat transfer into or out of the system occurs. Isochoric Process – A process where no change in volume occurs and the system does no work. Isobaric Process – A process in which no change in pressure occurs. Isothermal Process – A process in which no change in temperature occurs.