Absolute Zero
Thermodynamics Part 2
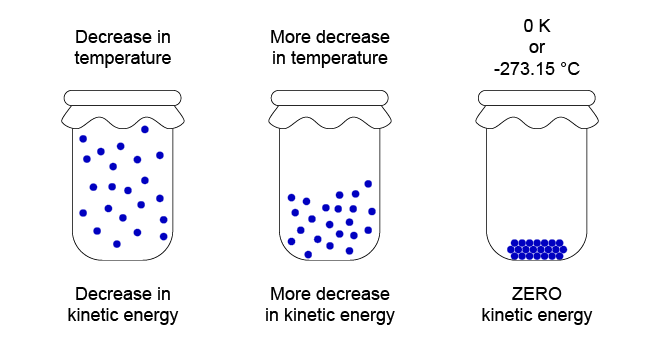
Third law The third law of thermodynamics states: As the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, all processes cease and the entropy of the system approaches a minimum value. This law of thermodynamics is a statistical law of nature regarding entropy and the impossibility of reaching absolute zero of temperature. This law provides an absolute reference point for the determination of entropy. The entropy determined relative to this point is the absolute entropy. Alternate definitions include “the entropy of all systems and of all states of a system is smallest at absolute zero,” or equivalently “it is impossible to reach the absolute zero of temperature by any finite number of processes”. Absolute zero, at which all activity would stop if it were possible to achieve, is −273.15 °C (degrees Celsius), or −459.67 °F (degrees Fahrenheit), or 0 K (kelvin), or 0° R (degrees Rankine).