(click to open)
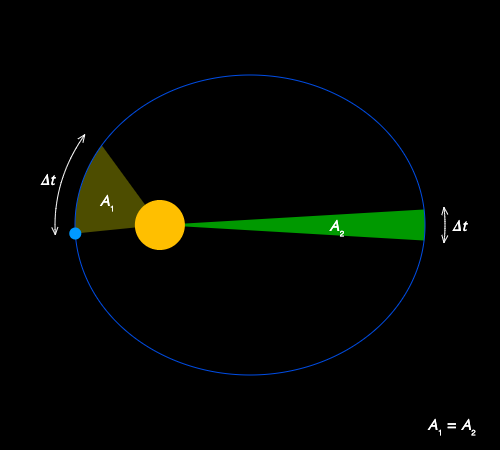
Second Law
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
- The Law of Areas: A line that connects a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. Kepler’s second law states, “The radius vector drawn from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time”. As the orbit is not circular, the planet’s kinetic energy is not constant in its path. It has more kinetic energy near the perihelion, and less kinetic energy near the aphelion implies more speed at the perihelion and less speed (v_min) at the aphelion.